Table of Contents
Cisco Best Practice
or What we really use!
- vlans (802.11q)
- stp
- snmp → mrtg
- security - dhcp helper
- more static arp
STP - What it solves?
Something's missing, something's redundant?
- missing - broken cable, lost connection, broken switch
- redundant - badly placed cable, circles the network
STP can fix all of the above.
Redundant layer 2 redundacy problems
- broadcast storm
- multiple frame copies - which is basicly the same
- ARP table instabilities (Cisco: CAM table)
Magic question - what is 32768?
Time tracking
- 20 waiting for no BPDU
- 15 unblock blocked ports and listening state for new BPDUs - topology change
- 15 learning state, accepts all ethernet frames, learns MAC, but doesn't forward
First we obviously need to know, how to disable stp for end host device (designated forwarding port).
conf t
int fa 0/5
spanning-tree portfast
end
Creating broadcast storm
First create a loop, then we disable stp and finaly one ping will send arp broadcast. Lets suppose the loop goes from port fa0/5 somewhere. Clear the counters and check the state of interface
show interface fa0/5 clear counters show interface fa0/5
no spanning-tree vlan 1
And check vlans by
show vlan brief
Assign random IP to layer 3 interface vlan 1 and ping
conf t
int vlan 1
ip 1.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
no shut
end
Check it by
show ip int brief | ex una
and ping, just once
ping 1.0.0.2 repeat 1
Check the interface with loop on vlan 1
show interface fa0/5
STP
PVST+ - VLAN time
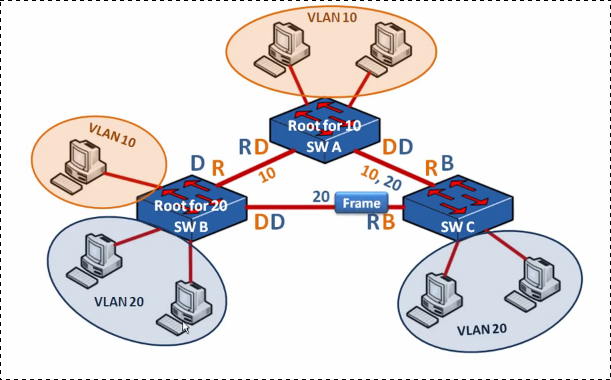
 We make switch A root for VLAN 10
We make switch A root for VLAN 10
spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 16384
And switch B root for VLAN 20
spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree vlan 20 priority 16384
RSTP - Is STP slow?
Yes, it is. New version Rapid STP doesn't have blocking port, rather has alternate port. Theory goes on the table, practicaly you doesn't have to know anything. Just type
spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
Can I see STP?
show spanning-tree vlan 98
Little security
Let's suppose you're running an office network with STP. What if someone sent bad BPDU frames to you switches? He could re-route all the traffic throught his black-hat-notebook

You can filter or guard incomming BPDU packets
- filter - ignores and discard the packet
- guard - the port is put in the error-disabled state
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable
There is no more or less static arp, but the interval could be longer.